Traditionally, freight and cargo handlers remove cartons by hand to swap out pallets. This manual approach is time-consuming and labor-intensive, which is why pallet inverters have become a viable solution.
Pallet inverters simplify and accelerate cargo handling by providing an automated solution for removing or swapping pallets. As a result, carriers and shipping companies save valuable time, money, and resources.
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the topic of pallet inverters and explain how they work. We’ll also share the key benefits and drawbacks of using them and their expected return on investment.
What Are Pallet Inverters?
A pallet inverters, also called a pallet changer or pallet exchanger, is a type of handling equipment that rotates pallets with their loads. They’re designed to simplify pallet swapping or exchanging – the process of transferring products from one pallet to another.
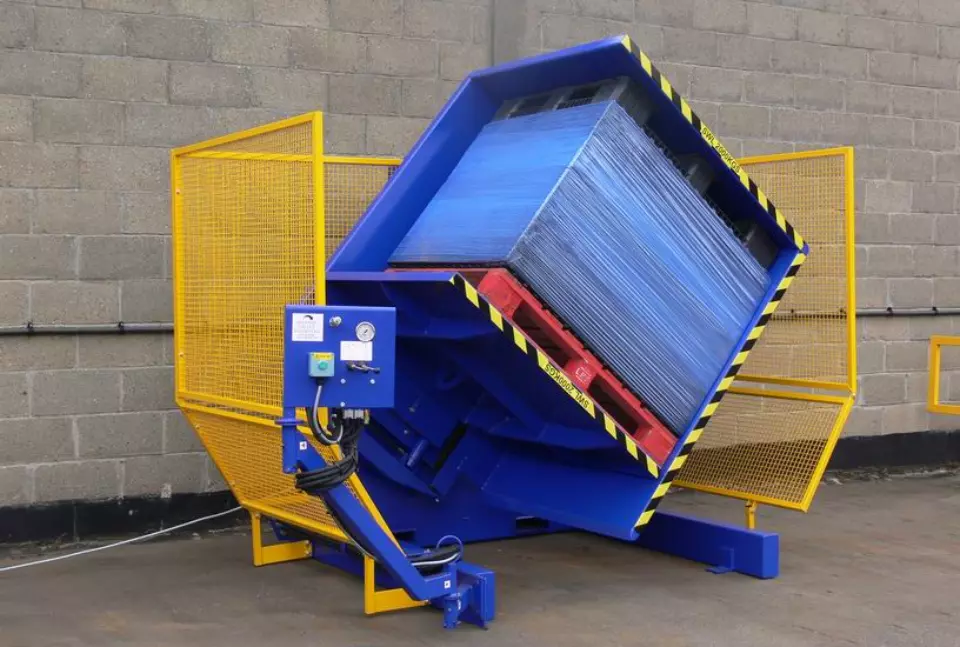

Today, various pallet inverters are available in the market for carriers and logistics companies to choose from. However, they are split into two main categories – mobile and stationary pallet inverters.
Mobile pallet inverters are portable and can be moved to different locations within a facility. On the other hand, stationary pallet inverters are mounted onto the floor, which means they are typically integrated into a specific part of the warehouse or factory.
These inverter types vary in load capacity, maximum cargo length, orientation angle, and degree of mechanization or automation. Most users install them in warehouses near cargo staging or processing areas. Many warehouses have multiple mobile and stationary inverters to accommodate handling demands.
They’ve been adopted by various industries and they form part of a core supply chain process to handle, rotate, and reposition goods efficiently. Examples of industries include food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and retail. Below are the two main features these handling machines provide:
- Exchanging Pallets – Pallet changers can help handlers exchange pallets that are damaged or that need to be returned to the shipper. They make the process simpler and quicker.
- Shifting Loads – Pallet exchangers also enable cargo handlers to reconfigure and rearrange cartons, barrels, or other types of loads manually once the inverter tilts the cargo.
How Do Pallet Inverters Work?
The core function of pallet inverters is to rotate pallets together with their loads (typically products or cartons). Cargo handlers place the pallet with its content onto the base frame, usually with a forklift or an electric pallet jack.
The hydraulic clamping mechanism actuates the clamping plate (located at the top and attached to the frame), which is lowered until it makes contact with the cargo. Many modern exchangers have sensors to ensure the clamp exerts too much force on the cargo.
The pallet inverter then rotates the pallet and its load anywhere between 90 and 180 degrees to remove and replace damaged pallets and reorientate products. Once completed, they rotate the pallets to their initial position and remove them using a forklift or an electric pallet jack.
Benefits of Using Pallet Inverters
Pallet inverters offer many benefits to handlers, shipping and logistics companies, storage facilities, and manufacturing plants. Let’s explore some of these benefits in more detail.
- Provides Long-Term Cost Savings – Labor can be costly, even in off-peak seasons. As a result, logistics companies and carriers incur high costs to hire full-time resources that handle cargo. While pallet inverters require an initial investment, they offer a more cost-effective solution in the long run, saving valuable time and money.
- Reduces Safety Risks – Safety is a major aspect of any logistics and supply chain operation. Pallet inverters reduce manual labor when lifting heavy loads, fostering a safer working environment.
- Is More Space-Efficient – Manually exchanging products on pallets can require a lot of floor space, as workers need room to arrange or rearrange goods. Mobile and stationary inverters can complete the task using less space, allowing handlers to improve operational efficiency.
- Increases Productivity – Swapping out pallets with manual labor usually involves unwrapping and shifting pallets one at a time, making the process time-intensive, especially when working with smaller items in large quantities. Pallet inverters can swap pallets in a matter of seconds, saving handlers valuable time to improve operational productivity.
- Lowers Cargo Damage Risks – Handling cargo manually or using forklifts increases the risk of cargo damage or mishandling. Pallet inverters greatly reduce these risks by automating handling and saving companies on insurance and damage expenses.
Drawbacks of Using Pallet Inverters
Like any other logistics solutions, pallet inverters aren’t without a few drawbacks, which we’ll be outlining in the section below.
- Higher Upfront Costs – Procuring pallet inverters requires an initial investment. As a result, many companies stick to manual cargo handling, even if switching to inverters would provide a good return on investment. Some smaller logistics companies may not have the capital requirements to cover the upfront costs.
- Operating Knowledge – Equipping a facility with pallet inverters doesn’t guarantee efficiency enhancement, as cargo handlers must be proficient in operating them. Therefore, companies must invest in extensive training to ensure handlers follow standard operating procedures (SOPs).
- Power Consumption – Pallet exchangers require power consumption and ultimately increase electricity bills. They’re equipped with powerful electric motors, hydraulic actuators, and different sensors that require power. Therefore, logistics companies should consider the added expenditures.
- Requires Maintenance – Like any cargo handling machine or equipment, pallet inverters require regular maintenance and occasional repairs. Untimely malfunctions can lead to process disruption, damage, delays, and other issues.
- Product Limitations – Most economical pallet inverters are unsuitable for handling fragile or sensitive cargo, especially items vulnerable to damage due to pallet orientation. For instance, glass products may crack or break during this process. Therefore, it’s important to consider the application of these pallet inverters and be mindful of what products or commodities they’re used for.
Pallet Exchanger Costs
Pallet inverters vary significantly depending on various factors, including make and model, load capacity, type, features, and condition (new or used). As such, companies have multiple options to choose from. On average pallet inverters typically cost between $8,000 and $30,000.
You can also find higher-end models offering more automated features, increased durability, and extended applications exceeding $100,000. However, these are more common in multinational companies with large-scale operations.
Along with the initial investment, companies should also consider the recurring costs, including maintenance, repairs, training, and power consumption. Local regulations can also influence the overall costs, especially when importing these inverters from other countries.
What’s the Expected ROI?
The return on investment (ROI) of a pallet inverter depends on many factors, including labor costs, process efficiency, and overall profitability. Companies that take advantage of pallet exchangers typically save anywhere between $40,000 to $80,000 annually per inverter, by reducing labor and other equipment costs.
Depending on the type of machine and the efficiency of the existing operation, an investment in a pallet inverter can break even within about 6 to 12 months.
Get Free Course Access
If you enjoyed the article, don’t miss out on our free supply chain courses that help you stay ahead in your industry.

Andrew Lin
Co-Founder & Writer
at freightcourse
About the Author
Andrew is a multi-business owner with over 12 years of experience in the fields of logistics, trucking, manufacturing, operations, training, and education.
Being the co-founder of freightcourse has given him the ability to pursue his desire to educate others on manufacturing and supply chain topics.
Follow us